CIVICS NOTES
FORM ONE-TOPIC ONE
OUR NATION
Prepared by Sir.Albert J.Safari
Mobile contact:+255 715 803 005
Mail Address:salbertode@
yahoo.com
When two people of the opposite sex get together as husband and wife, they form a family. A family is social group of people who are closely related to each other. A combination of various families forms a Clan. A group of different clans form tribes who have the same Culture, History and Language. The combination of various tribes makes up the population of a nation.
FORM ONE-TOPIC ONE
OUR NATION
Prepared by Sir.Albert J.Safari
Mobile contact:+255 715 803 005
Mail Address:salbertode@
yahoo.com
When two people of the opposite sex get together as husband and wife, they form a family. A family is social group of people who are closely related to each other. A combination of various families forms a Clan. A group of different clans form tribes who have the same Culture, History and Language. The combination of various tribes makes up the population of a nation.
A Nation can be defined as alarge group or community of people living in a defined geographical area and sharing a common history, culture and language under one government. Examples of nations includeTanzania, Japan, Zimbabwe, India and Uganda. A nation should be recognized by other nations as a sovereign state andshould be free to decide and implement its own policies. It should not be part of another nation nor should it be under the control of another nation.
The Components of our Nation
The Components that Make up our Nation
To be able to analyse the components that make up our nation
For any nation to be recognized as a nation it must have the following components: Sovereignty, People, culture, boundaries and government
Sovereignty
The word “Sovereignty” comes from the Latin word “superanus”, which means “supreme”. Therefore, Sovereignty refers tothe supreme power exercised by anation to control all individuals and associations within itsterritory.
Sovereignty can also be defined as the highest power which belongs to the people. National sovereignty means that a nation is free to decide and implement its decisions without being interfered with by any external forces from other nations. A nation should be able to run its political, economic and social matters independently.
Importance of National sovereignty
- National sovereignty is important because it maintains good relations with other nations through promoting good foreign policies on matters concerning other nations.
- It helps maintain peace and security of a nation through execution of national laws, rules and regulations to prevent civil wars and conflicts with other nations.
- It brings about national stability and encourages investors to invest in a country because a national is free to establish policies that will encourage local and foreign investors to invest in the country.
- Citizens are free from being dominated by other nations because of non-interference in the control of the nation by other countries.
Hindrances to national sovereignty
- Poverty. This is the inability to afford basic needs like food, shelter and clothing which is the main problem faced in many African countries whereby most are economically poor. This results in African countriesdepending on developed countries for help through grants and aid which create conditions that violate the sovereignty of some African countries.
- Civil wars. The fighting between ethnic groups within the same nation can affect the freedom of the nation because when the nation fails to maintain peace and security within the nation, United Nations will intervene to protect human rights.
- Natural hazards. Disasters such as floods, earthquakes and volcanic erruptions undermine the economies of poor countries which in turn hinders national sovereignty since the government cannot depend on its own capabilities and needs toask for assistance from other countries through aid.
Population
Population is the number of people living in a particular defined area. According to the 2010 population survey report, Tanzania has over 40 million people. More than 80% of Tanzania's population lives in rural areas. Tanzania mainland has over 125 ethnic groups. Kiswahili is the common language and the largest population group is Bantu who occupy approximately two-thirds of the country and are divided into many tribes. Within the population is where we can find leaders, citizens and the army which protects the country and builds up a strong nation.
Boundaries
National boundaries are the dividing lines between the area belonging to Tanzania and the area belonging to her neighboring countries. Tanzania was formed on the 26th April 1964. On that day, Tanganyika and Zanzibar united to form thecountry currently known asTanzania. Our country Tanzania covers a total area of 945,202 square kilometersand is bordered by man-made and natural boundaries. Natural boundaries of Tanzania includethe Indian Ocean to the East, Mount Kilimanjaro to the North, Ruvuma River to the South, Lake Nyasa to the south west, and Lake Victoria to the North and Lake Tanganyika to the West.
Tanzania is bordered by eight nations, namely Kenya and Uganda to the North, Rwanda, Burundi and Democratic Republic of Congo to the West, Mozambique to the South, Malawi and Zambia to the South West. The Indian Ocean borders Tanzanian’s Eastern side. The islands of Zanzibar and Pemba lie along the coast of Tanzania Mainland.
Map of Tanzania showing the national boundaries.
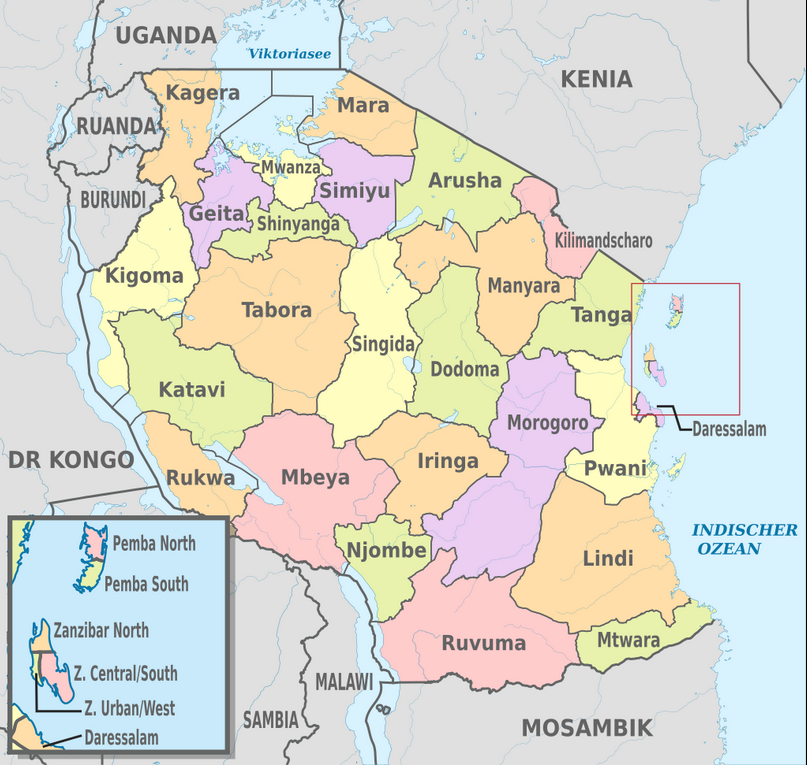
The Government
The government is an administrative organ of the state. It consists of elected and selected groups of people who are responsible for controlling and maintaining the laws and orders of acountry. The state has three organs which assist each other in fulfilling its functions. These organs are:
- The Executive.The Executive is the main branch of the central government andcomprises of the president, the cabinet, civil servants and armed forces. The Executive is responsible for administering various activities of the government.
- Judiciary. Thisorgan functions to interpret the laws and make rulings over disputes in the state.
- Legislature is the law making body of the state. It is the state organ whose members are elected to represent different constituencies. Some of them are appointed. Legislature is also called parliament and is comprised of the President and the National Assembly. The President is part of the parliament but not a member of the parliament. This is because the president does not participate in parliamentary discussions but participates in the process of making laws by signing the bills to become laws.
Culture
Refers to the customs and beliefs of a particular group of people. It also includes the people`s way of life and social organization.
Exercise 1
Answer the following questions
- In your own words, explain what you understand by the term Nation and give five examples of the nations you know apart from the examples given above.
- Suggest five solutions to protect national sovereignty.
- Draw the map of Tanzania and show its national boundaries.
- Why is the President of the United Republic of Tanzania said to be part of the parliament but not the member of it in the national assembly?
- List five national components.
The National Symbols
Tanzania's National Symbols
Identify Tanzania's national symbols
What is a national symbol?
A symbol is a sign that represents something. National symbols are signs which represent a nation. These symbols are very important as they serve as a reminder of our nationhood to us and to the rest of the world; they promote our culture and remind us about events that have taken place in our nation. Tanzania has several symbols; these include tangible things like money, flags and the coat of arms,as well asintangible things like the national anthem and language.
The following are the major national symbols in Tanzania:
- The national flag
- Presidential standard
- The coat of arms
- National Anthem
- Uhuru Torch
- National currency
- National Language
- The national Constitution
- National festivals (holidays) in Tanzania
The Significance of each National Symbol
Explain the significance of each national symbol
The national flag
Anational flag is a piece of cloth with a special colour design. The national flag of Tanganyika was hoisted for the first time on the 9th December, 1961 and that of the United Republic of Tanzania was hoisted for the first time on the 26th April 1964, when Tanganyika and Zanzibar united to form Tanzania. The main function of the national Flag is to show that Tanzania is a completely independent and sovereign nation. Our Flag has four colors; Green, Yellow, Black and Blue.
- Green represents the land and vegetation of Tanzania
- Blue represents the ocean and other water bodies found in the country
- Black represents the people of Tanzania
- Yellow represent the natural wealth of Tanzania, like minerals
Tanzanian’s national flag.

Importance of national flag
- It is a symbol of our independence/sovereignty
- It is a symbol of freedom and unity of the people
- The National flag is also a symbol of the nationality and a symbol of Tanzania culture
Presidential standard
The presidential standard is a flag which is used during official ceremonies where the president is in attendance. It has a green background with a blue and the coat of arms in the middle. The coat of arms on the presidential standard has no crops, human figure or the peak of Mount Kilimanjaro.
The Presidential standard

The coat of arms
The coat of arms is an official seal or stamp of the government which comprises different colors and landmarks of Tanzania. It act as national badge and, therefore, all government publications bear this official seal. Our coat of arms has twelve components. These components represent various national interests such as state power, economic bases, national culture and history.
Compositions of the coat of arms
The coat of arms comprises of the following things:
- Two human figures – The man and the woman represent the people of Tanzania. The two figures also symbolize the need for cooperation between men and women in order to bring about development.
- Two elephant tusks – These represent our national heritage in terms of wildlife. Tanzania has beautiful national parks and game reserves in which different animals and plants are found in their natural habitats.
- Shield and spears – They represent weapons that were used by Tanzanians to resist colonialism. These weapons represent the readiness of the people to defend their independence
- Golden band on the upper part of the shield - This represent the mineral wealth of the country
- Uhuru Torch – It symbolizes freedom, enlightenment, knowledge and prosperity.
- National Flag –It represent our sovereignty.
- Red band on the shield- this represent the fertile red soil found in our country
- Crossed Axe and hoe – These represent the tools which Tanzanians use to develop their country.
- Sea waves – These represent water bodies found in Tanzania. Approximately 62,000Km square of Tanzanian`s total area is made up of water bodies. This includes the Indian Ocean, rivers, lakes and swamps.
- Peak of mount Kilimanjaro- This is the highest mount in Tanzania and Africa in general which represents attractive geomorphological features.
- Crops (cotton and gloves) – At the feet of the man there is a branch of a glove tree. At the feet of the women there is the branch of cotton plant which stands for the cash crops produced in Tanzania.
- The wards “Uhuru na Umoja” which means freedom and unity express the belief that, Tanzanian`s strength depends on people`s solidarity.
Importance of the coat of arms
- It is used as the symbol of the authority and official government seal.
- It symbolizes our national culture and history.
- It symbolizes state power.
The national coat of arms

National Anthem
This is the official song which reflects people`s national feelings, desire, glory and pride in their nationality. The Tanzanian national anthem is sung during important national occasions such as when a special announcement is made by the president; when foreign heads of states visit our country; When the president or the vice president and the prime minister visit another country officially, and when our national teams are playing against teams of other countries; before and after the president addresses the nation; and when the national flag is hoisted.
Importance of the national anthem
- It is a symbol of our nationality , freedom and it unifies Tanzanians
- It makes citizens feel proud of their country
- National anthem expresses a sense of belonging to Tanzania and Africa
- It identifies Tanzania outside the country.
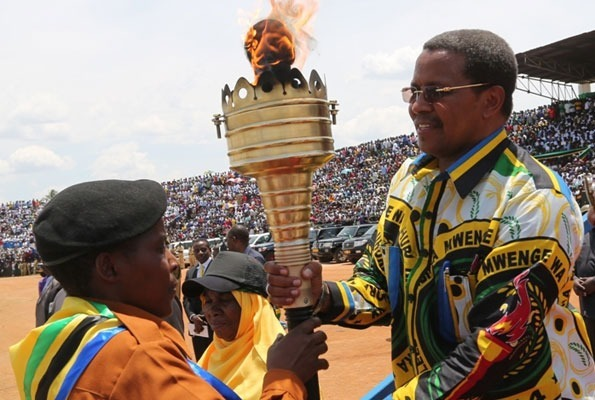
Uhuru Torch
This is the touch of freedom which also known as independence touch introduced by the first president of Tanzania Mwl. J.K.Nyerere as a symbol of freedom, unity, love, dignity, solidarity and hope among Tanzanians. It was first lit on top of Mount Kilimanjaro at midnight on 9th December 1961. This was the day Tanganyika got independence from Britain.
Importance of Uhuru Torch
- It symbolizes freedom and light
- It promotes unity in the country
- It also promotes peace, dignity, respect and hope among Tanzanians
- It promotes co-operation among Tanzanians and development in aspects of life
The Uhuru Torch

National currency
Is the system of money that a country uses. Our national currency is the Tanzanian shilling. Currency is also called money. Money is used for measuring value, trading and paying for goods and services in a country. Tanzania money is the form of notes and coins.
Importance of national currency
- It acts as a medium of exchange in trade transactions that is selling and buying of goods and services in the country
- It is used to measure value and identify the nationality and freedom of a nation
- It is the means of settling debts.
National Language
This is the language spoken by all the people within a country. The national language of Tanzania is Kiswahili.
Importance of the national language
- The national language acts as the media of communication within a county.
- It symbolizes the culture of the nation concerned which is Tanzania
- It unifies people with a common history.
- It also identifies the country internationally
The National Constitution
A national constitution is the system of laws and principles by which the nation is governed by. A constitution provides guidelines which society must follow. Our country Tanzania is ruled according to the constitution that was enacted 1977. Since that time year, it has been undergoing some amendments to suit the contemporary needs.
Importance of the national constitution
- The government rules by the will of the people through the constitution
- The constitution is the basic law from which all other laws are created.
- Under constitution there is separation of power between the executive, the legislature and the judiciary.
- The constitution provides for elections through which the people elect their representatives in the government
- The constitution gives people the freedom to enjoy their right.
- The constitution provides individuals with the mechanism to claim their rights before the courts of law.
The cover of the constitution of Tanzania 1977

Tanzania's National Festivals and their Significance
Identify Tanzania's national festivals and their significance
National festivals are special public days created by the state which exempt people from doing any government or official work and therefore people are expected to rest. In Tanzania these days are called Public holidays.
Types of national days
Religious public days
These days are marked by special religious events or festivals according to the beliefs and faith of particular group of people. In Tanzania there are two dominant religious, namely Christianity and Islamic. The public holidays associated with these religious are;
- Christmas day - falls on 25th December each year
- Easter holiday – depends on Christian calendar
- Eid-el-Fitri and Eid –el-Haj – Depend on Islamic calendar and sighting of the moon
- Boxing day – Falls on 26th December each year
Political public holidays
These are special days that commemorate events which have profound meaning politically. Sometimes they are known as civic national festivals and holidays Political public holidays in Tanzania are;
- Independence day – falls on December 9th each year
- Union day – fall on 26th April each year
- NaneNane day – Falls on 8th August each year
- Zanzibar Revolution Day – falls on 12th January each year
- Nyerere Day – falls on 14th October each year
- Karume Day – falls on 7th April each year
- Sabasaba Day – falls on 7th July each year
Universal public days
These are special days for the rest and celebration for all people in the world. These universal holidays are;
- New Year – falls on 1st January each year
- Workers day/ labour day – falls on 1st May each year
Importance of national festivals/ public days
The followings are the Importance of national festivals/ public days;
- These days mark important events in our country
- The celebration keep the history alive since Tanzania are reminded of what has taken place in their country
- During these events leaders pass important information to the public
- Public celebration provides an opportunity for citizens to meet and share views, experience and knowledge.
- Celebrating together enhance the unity of Tanzanians.
- Annual celebrations impart on Tanzanians the culture of commemorating important national events.
- These events helps the leaders to identify problems in the society as citizens highlight their problems through speeches, posters, drama or songs.
Exercise 2
Answer the following questions
- With examples mention three types of national festivals in Tanzania
- When do farmers and traders exhibit their agriculture products, implements and machinery?
- What are the importance of national constitution?
- Mention any five compositions of the coat of arms and explain what each component represent.
- Name various occasions you know where the national
- anthem is always sung.
- The Tanzania national flag has four colors:
- Black represents ---------------------
- Yellow represents -------------------
- Blue represents ---------------------
- Green represents --------------------
- Why is it important to respect national symbols?
- Mention three uses of coat of Arms
- Why do you think it is important to have the union government of Tanzania and Zanzibar?
- When the first constitution of the United Republic of Tanzania was written?

